Systems manager: Systems Manager: 7 Ultimate Power Roles in Tech Leadership
If you’ve ever wondered who keeps the digital backbone of a company running smoothly, meet the systems manager — the unsung hero of modern tech operations.
What Is a Systems Manager?

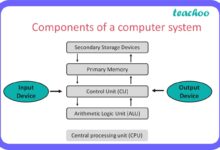
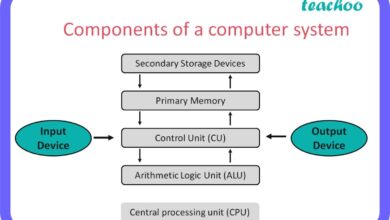
A systems manager is a pivotal professional responsible for overseeing the design, implementation, and maintenance of an organization’s IT infrastructure. This role ensures that hardware, software, networks, and data systems work cohesively to support business goals. As technology evolves, so does the scope of what a systems manager does — from managing on-premise servers to orchestrating cloud-based ecosystems.
Core Definition and Scope
The term ‘systems manager’ may vary slightly depending on the industry, but at its core, it refers to someone who manages integrated systems that support business operations. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, these professionals often work closely with network architects and IT directors to ensure seamless system functionality.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Responsible for system stability, security, and performance
- Acts as a bridge between technical teams and executive leadership
- Manages both legacy and emerging technologies
“A systems manager isn’t just a tech expert — they’re a strategic thinker who aligns technology with business outcomes.” — TechLeaders Journal, 2023
Evolution of the Role Over Time
Originally, systems managers focused primarily on mainframes and internal server networks. In the 1980s and 1990s, their responsibilities were largely confined to data centers. However, with the rise of cloud computing, mobile integration, and cybersecurity threats, the role has expanded dramatically.
Today’s systems manager must understand not only traditional IT systems but also DevOps practices, automation tools, and compliance frameworks like GDPR or HIPAA. The shift toward remote work has further increased demand for systems managers who can maintain secure, scalable infrastructures across distributed environments.
Key Responsibilities of a Systems Manager
The day-to-day duties of a systems manager are diverse and dynamic. They span technical oversight, team leadership, and strategic planning. These responsibilities are critical to ensuring that an organization’s technological foundation remains robust and adaptable.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
System Design and Implementation
One of the primary roles of a systems manager is designing IT architectures that meet current and future business needs. This includes selecting appropriate hardware, software, and network configurations.
- Conducts needs assessments to determine system requirements
- Oversees the deployment of new systems or upgrades
- Integrates third-party applications and APIs
For example, when a company migrates from on-site servers to AWS or Azure, the systems manager leads the planning and execution process, ensuring minimal downtime and data integrity.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Once systems are live, ongoing maintenance becomes crucial. Systems managers schedule regular updates, apply security patches, and monitor system health using tools like Nagios, SolarWinds, or Zabbix.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
When issues arise — such as server outages or network latency — the systems manager coordinates troubleshooting efforts. They analyze logs, identify root causes, and implement fixes, often under tight deadlines.
“Downtime costs businesses an average of $5,600 per minute.” — Gartner, 2022
This statistic underscores the importance of proactive system monitoring and rapid response capabilities managed by skilled systems managers.
Security and Compliance Oversight
In an era of frequent cyberattacks and data breaches, systems managers play a vital role in safeguarding organizational assets. They implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols to protect sensitive information.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Additionally, they ensure compliance with regulatory standards such as:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
- SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act)
- PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
Regular audits, risk assessments, and employee training programs are part of their security strategy.
Essential Skills for a Successful Systems Manager
Becoming an effective systems manager requires a blend of technical expertise, leadership ability, and problem-solving acumen. While certifications and education provide a foundation, real-world skills determine long-term success.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Technical Proficiency
A systems manager must be fluent in multiple areas of IT infrastructure. Key technical competencies include:
- Operating systems (Windows Server, Linux, Unix)
- Networking (TCP/IP, DNS, VLANs, firewalls)
- Cloud platforms (AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform)
- Virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V)
- Scripting and automation (PowerShell, Bash, Python)
For instance, automating routine tasks through scripts reduces human error and frees up time for strategic initiatives. A systems manager proficient in Python can create custom monitoring tools or automate backup processes.
Resources like Coursera’s IT Automation with Python course help professionals build these in-demand skills.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Leadership and Team Management
Unlike pure technicians, systems managers lead teams of system administrators, network engineers, and support staff. They delegate tasks, set performance goals, and mentor junior employees.
Effective leadership involves:
- Clear communication of technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders
- Conflict resolution within technical teams
- Project management using methodologies like Agile or ITIL
A systems manager must inspire confidence during high-pressure situations, such as system failures or security incidents.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Problem-Solving and Analytical Thinking
When systems fail, the systems manager is the first line of defense. Strong analytical skills allow them to dissect complex problems and develop efficient solutions.
They use diagnostic tools, log analysis, and performance metrics to identify bottlenecks or vulnerabilities. For example, if a database query slows down operations, the systems manager investigates indexing issues, server load, or network latency.
“The best systems managers don’t just fix problems — they anticipate them.” — CIO Magazine, 2023
Systems Manager vs. Other IT Roles
While the title ‘systems manager’ might sound similar to other IT positions, it carries distinct responsibilities and scope. Understanding how this role differs from others helps clarify its unique value.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Comparison with System Administrator
A system administrator focuses on the hands-on operation of IT systems — installing software, managing user accounts, and performing backups. In contrast, a systems manager takes a broader view, focusing on strategy, architecture, and long-term planning.
Think of it this way: the system administrator keeps the engine running; the systems manager designs the entire vehicle.
According to CompTIA, system administrators typically report to systems managers in mid-to-large organizations.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Differences from Network Engineer
Network engineers specialize in designing and optimizing network infrastructure — routers, switches, firewalls, and connectivity protocols. While systems managers may oversee network operations, their focus extends beyond networking to include servers, storage, applications, and cloud services.
In smaller companies, one person might wear both hats, but in larger enterprises, these roles are clearly separated.
Contrast with IT Director
The IT director is a higher-level executive responsible for the entire IT department’s budget, strategy, and alignment with corporate goals. A systems manager often reports to the IT director and executes the technical vision set by leadership.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
While the IT director deals with boardroom-level decisions, the systems manager operates at the operational-strategic intersection, translating vision into action.
Industries That Rely on Systems Managers
Systems managers are essential across a wide range of sectors. Any organization that depends on digital infrastructure needs skilled professionals to manage its systems effectively.
Healthcare and Medical Systems
In healthcare, systems managers maintain electronic health record (EHR) systems, telemedicine platforms, and patient data security. With strict HIPAA regulations, they ensure that all systems comply with privacy laws.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
They also integrate medical devices with hospital networks, requiring deep knowledge of both IT and biomedical systems.
Finance and Banking Sector
Banks and financial institutions rely on systems managers to protect transaction systems, manage core banking software, and prevent cyber fraud. Given the high stakes, redundancy, failover systems, and real-time monitoring are critical.
Systems managers in finance often work with fintech platforms, blockchain integrations, and high-frequency trading systems that require ultra-low latency.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Education and E-Learning Platforms
Universities and online learning providers depend on systems managers to maintain learning management systems (LMS), student information systems (SIS), and virtual classroom technologies.
During the pandemic, many educational institutions accelerated digital transformation, increasing the demand for systems managers who could scale infrastructure rapidly.
How to Become a Systems Manager
Becoming a systems manager typically follows a structured career path that combines education, certifications, and hands-on experience.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Educational Requirements
Most systems managers hold at least a bachelor’s degree in:
- Computer Science
- Information Technology
- Management Information Systems (MIS)
Some pursue advanced degrees like an MBA with a technology focus to enhance leadership credentials. Universities such as MIT and Stanford offer specialized programs in IT management.
Relevant Certifications
Certifications validate technical expertise and are highly valued in the industry. Top certifications for systems managers include:
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- CompTIA A+ and Network+
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate
- Cisco CCNA or CCNP
- VMware VCP
- ITIL Foundation
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
These credentials not only boost employability but also demonstrate commitment to professional development. Platforms like Udemy and Pluralsight offer prep courses for these exams.
Career Progression Path
Many systems managers start as help desk technicians or junior system administrators. With experience, they advance to senior technical roles before moving into management.
A typical progression looks like:
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Help Desk Technician → System Administrator → Senior Systems Engineer → Systems Manager → IT Director
Networking, mentorship, and continuous learning are key to accelerating this journey.
Challenges Faced by Systems Managers
Despite the rewarding nature of the role, systems managers face numerous challenges in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
Keeping Up with Rapid Technological Change
Technology evolves at breakneck speed. New tools, frameworks, and security threats emerge constantly. Systems managers must stay updated through continuous learning, attending webinars, reading industry publications, and participating in tech communities.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
For example, the shift to containerization (e.g., Docker, Kubernetes) requires systems managers to learn orchestration platforms and microservices architecture.
Balancing Security and Accessibility
One of the toughest balancing acts is securing systems without hindering user productivity. Overly restrictive policies can frustrate employees, while lax security opens the door to breaches.
Systems managers implement solutions like multi-factor authentication (MFA), zero-trust models, and role-based access control (RBAC) to strike the right balance.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Managing Remote and Hybrid Workforces
Post-pandemic, many organizations operate in hybrid or fully remote models. This increases the complexity of managing endpoints, securing home networks, and ensuring reliable access to cloud resources.
Systems managers now deploy virtual private networks (VPNs), endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, and cloud identity management (e.g., Microsoft Entra ID) to support distributed teams.
Future Trends Shaping the Systems Manager Role
The role of the systems manager is not static. Emerging technologies and business trends are reshaping what’s expected from these professionals.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Automation and AI Integration
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming IT operations. AI-driven monitoring tools can predict system failures before they occur, allowing systems managers to act proactively.
Tools like AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations) analyze vast amounts of log data to detect anomalies and suggest remediation steps. This reduces manual workload and improves system reliability.
Cloud-Native and Hybrid Architectures
More organizations are adopting hybrid cloud models — combining on-premise infrastructure with public and private clouds. Systems managers must master multi-cloud management platforms and ensure seamless interoperability.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
They also need to optimize costs, as cloud spending can spiral without proper governance. Tools like AWS Cost Explorer and Azure Cost Management help track usage and eliminate waste.
Increased Focus on Cybersecurity Resilience
With ransomware attacks growing in frequency and sophistication, systems managers are expected to build resilient systems capable of withstanding and recovering from cyber incidents.
This includes implementing robust backup strategies, disaster recovery plans, and incident response protocols. Regular penetration testing and employee phishing simulations are now standard practices.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
What does a systems manager do?
A systems manager oversees the design, implementation, and maintenance of an organization’s IT systems. They ensure that hardware, software, networks, and data centers operate efficiently, securely, and in alignment with business objectives. Their role includes troubleshooting, security management, team leadership, and strategic planning.
How is a systems manager different from a system administrator?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
While both roles deal with IT infrastructure, a system administrator handles day-to-day operations like user support and software updates, whereas a systems manager focuses on strategic planning, system architecture, and team leadership. The systems manager typically has broader responsibilities and higher-level decision-making authority.
What certifications are best for aspiring systems managers?
Top certifications include Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate, CompTIA Network+, Cisco CCNA, VMware VCP, ITIL Foundation, and CISSP. These credentials validate technical and managerial expertise in system operations, networking, cloud platforms, and security.
Is a degree required to become a systems manager?
While not always mandatory, most employers prefer candidates with a bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field. Advanced roles may require an MBA or master’s degree, especially in large organizations.
What industries need systems managers?
Systems managers are vital in healthcare, finance, education, government, retail, and technology sectors. Any organization that relies on digital infrastructure — which is nearly all of them — needs skilled systems managers to maintain and optimize their IT systems.
The role of a systems manager is more critical than ever in our interconnected world. From ensuring system uptime to leading digital transformation initiatives, these professionals are the backbone of modern IT operations. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the responsibilities and expectations placed on systems managers. By mastering technical skills, embracing leadership, and staying ahead of industry trends, aspiring systems managers can build rewarding careers at the forefront of innovation.
Further Reading: